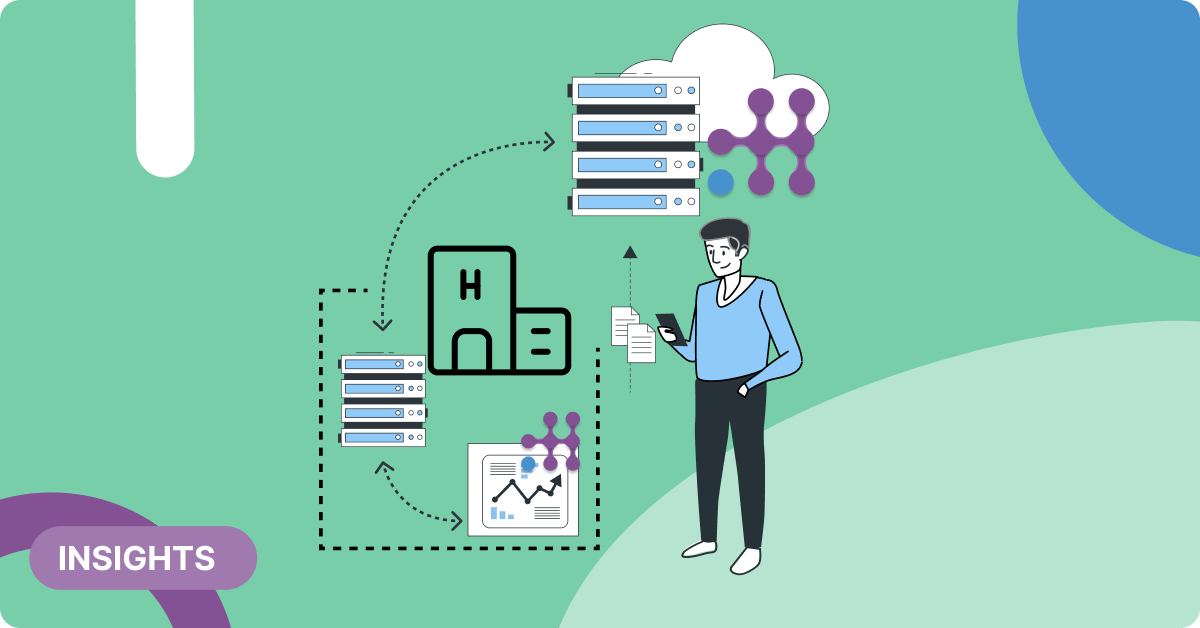
In many cases, clinical data cannot leave the premises of the healthcare organization that collects it. The comprehensive suite of Healthentia platform services for managing and processing data cannot address this issue. Instead, Innovation Sprint addresses the issue with specialized Healthentia edge services that facilitate data management and processing at the clinical data source. Thus, we increase the capabilities and resources at the hands of healthcare professionals, when they are working with data from different clinical sources, but also when mixed with real-world data from Healthentia. Specifically, the Healthentia edge services offer operational improvements in two important aspects, the provision of clinical data in the familiar Healthentia portal application, and the learning and use of composite clinical and behavioral models.
The Healthentia subject-level dashboard is enriched with clinical data using the Local Data Connector (LDC). LDCs are installed at hospital premises to facilitate the proper visualization of clinical data about a particular patient in the Healthentia subject-level dashboard, while the clinical data remains at the edge, without being ingested into the Healthentia platform. As a result, healthcare professionals have at their disposal a richer set of resources (composite clinical and real-world data analytics), improving their analytics experience by eliminating the need to use different tools and offering them more decision capabilities. LDCs are configured per hospital, to abstract the particularities of hospital information systems and create a message to be consumed by the browser, rendering the visualizations using metadata in the message along with the actual payload to be displayed.
The learning of composite clinical and behavioral models is also done at the edge (premises of the healthcare institution) utilizing edge installations of the Local Learning Services (LLS). The LLS facilitates model learning at the edge, employing the Innovation Sprint algorithms at the premises of the healthcare institutions, combining there the clinical and the Healthentia real-world data, formatting it into feature vectors suitable for learning models, and running the machine learning algorithms. The application of the resulting composite clinical and behavioral models enhances the healthcare professionals’ decision capabilities.
The use of the composite models is also done at the edge, employing the Local Inference Services (LIS) Healthentia edge service. LIS is an online service that also builds composite vectors, this time for online inference. The LIS then performs inference and transmits the inference results to the Healthentia platform.
The first version of the LDC and the LLS is being built in the context of the TERMINET project, as part of the TERMINET edge architecture. Stay tuned for news on their application in the SUPERO study that is now starting to enroll its first patients!